
May. 21, 2025

Study on Element Segregation and Grain Distribution Characteristics of Aluminum and Copper Wire Melting Marks
MEN Tengteng, LIU Shushuai, LIU Haixu, WANG Yongming
Study on Element Segregation and Grain Distribution Characteristics of Aluminum and Copper Wire Melting Marks
Through electron microprobe element analysis and electron backscatter diffraction analysis, a study was conducted on the micro-area element segregation and grain distribution morphology of aluminum and copper wire melting marks caused by fire and short circuits. The results showed significant iron element segregation in both fire-induced and short-circuit-induced melting marks of aluminum wires, but with different distribution patterns: iron elements formed coarse ring-like structures in fire-induced marks, while they appeared as elongated chain-like structures in short-circuit-induced marks. For copper wires, both fire-induced and short-circuit-induced melting marks exhibited oxygen element segregation, with distinct oxide morphologies: oxides in fire-induced marks were concentrated and mainly appeared as elongated rod-like or point-like structures, whereas in short-circuit-induced marks, they were dispersed and mainly spread in a network-like pattern. Additionally, there were notable differences in grain distribution and orientation between fire-induced and short-circuit-induced melting marks of both aluminum and copper wires. Fire-induced marks were dominated by coarse equiaxed grains or dendrite-like structures, while short-circuit-induced marks were mainly characterized by coarse columnar grains. It is worth noting that grain growth in short-circuit-induced marks exhibited a clear preferential orientation, whereas no such preference was observed in fire-induced marks.
aluminum wire melt marks / copper wire melt marks / grain distribution / micro area component / failure analysis {{custom_keyword}} /

Fig.5 Elemental segregation distribution of fire-burned melt marks on aluminum wire图5 铝导线火烧熔痕元素偏析分布 |
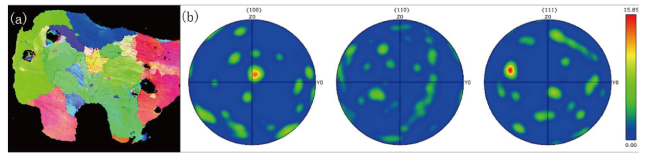
Fig.7 Typical orientation distribution (a) and polar chart (b) of fire-burned melt marks on aluminum wire图7 典型铝导线火烧熔痕取向分布图(a)与极图(b) |

Fig.9 Elemental segregation distribution of fire-burned melt marks on copper wire图9 铜导线火烧熔痕元素偏析分布 |

Fig.11 Orientation distribution (a) and pole figure (b) of fire-burned melt marks on copper wire图11 铜导线火烧熔痕取向分布图(a)与极图(b) |
| [1] |
王星尹, 叶益昌, 宋遥, 等. 电气防火安全的研究[J]. 自动化应用, 2023, 64(14): 251-253.
(
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [2] |
杨基元. 烧死现场的勘验与重建1例[J]. 刑事技术, 2013(3): 71-72.
(
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [3] |
陈建宏, 李胜林, 李艳超. 微量物证在北京大兴“11·18”重大火灾事故调查中的应用[J]. 刑事技术, 2020, 45(5): 542-544.
近年来,具有重大社会影响的火灾、爆炸、矿难等生产安全责任事故时有发生。由于伤亡人数众多,此类事件极易引起社会关注,如何科学、高效地还原事件经过,考验着每一名刑事技术人员。2017年11月18日,北京市大兴区西红门镇发生重大火灾。刑事技术人员通过细致勘查发现冷库间内电气线路故障,准确提取冷库间墙面保温材料,使用气相色谱/质谱联用仪进行比对检验,迅速确定起火原因。墙面保温材料中释放出的五甲基二乙烯三胺与空气混合,在密闭空间内达到爆炸极限,遇包埋在聚氨酯保温材料内的电气线路短路发生爆炸。装修材料中挥发性有机物的爆炸比较罕见,总结刑事技术人员在微量物证现场勘查及检验鉴定中的工作经验,可以为以后类似案事件的处置提供重要参考。
(
At times, significant events of social impact occur with the liable production-safety accidents, e.g., fire, explosion and mine disaster. Usually, such events could attract high-profile social attention due to the large number of casualties. Consequently, it is crucial to timely adopt proper and efficient disposal into the events and relevant matters. On November 18, 2017, a heavy fire disaster happened in Daxing district of Beijing. By careful investigation, the criminal technicians found that one short-circuit incident took place inside a cold storage depot so that they collected the heat-resistant materials from the wall there and examined with gas chromatography mass spectrometry. Through contrast experiment, it was revealed that one explosion was resulted from the heat-resistant material releasing its-comprising pentamethyldiethylenetriamine (PMDETA) to the concentration among 1.1%-5.7% (V), the explosion threshold of the substance when it blended with air and fitly ignited with the short circuit occurring inside the polyurethane heat-resistant materials. Such an explosion was, albeit rare, set off with the volatile organic compound from decoration materials. References are hoped to provide for criminal technicians to tackle with similar cases through the here summarization of trace evidence scene investigation and inspection.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [4] |
叶诗茂, 王立芬, 阳世群, 等. 电气火灾中铜导线火烧痕的研究[J]. 理化检验-物理分册, 2007, 43(5): 226-231, 235.
(
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [5] |
周正, 李光耀, 孙振文, 等. 金属物证检验及其在法庭科学领域中的应用[J]. 刑事技术, 2024, 49(3): 304-312.
金属物证在法庭科学领域的应用由来已久,其检验通常归于微量物证的检验范畴。金属物证通常以金属颗粒、附着物或熔融态出现在杀人、盗窃、枪击、电气火灾等多种类型的案事件中,检验方法通常包括扫描电镜-能谱法、金相检验法、X射线荧光光谱法、电感耦合等离子体质谱法等多种方法。通过金属物证的检验,可以起到确定案事件性质、提供侦查线索以及完善证据链的作用。本文通过对近年来国内法庭科学领域金属物证检验文献进行提取,以知识图谱分析工具VOSviewer进行分析,就金属物证的多种检验方法进行综述,了解其在法庭科学领域的应用现状,旨在为涉案金属物证的提取和检验提供借鉴作用。
(
Metal evidence has been used in the field of forensic science for a long time, where it is commonly categorized as trace evidence and subject to rigorous testing. This type of evidence is frequently encountered in a diverse range of cases, including murder, theft, shootings and electrical fires. It can manifest as metal particles, attachments, or even in a molten state. The methods commonly employed in the analysis of metal evidence include scanning electron microscopy- energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry, metallography examination, X-ray fluorescence spectrometry, inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, among others. The examination of metal evidence serves multiple purposes, such as unraveling the nature of the case, offering valuable investigative leads, and enhancing the integrity of the evidence chain. In this study, we focus on extracting and analyzing the recent literature pertaining to metal evidence examination in the field of forensic science in China. By using the knowledge graph analysis tool VOSviewer, various metal evidence examination methods are summarized to understand their application status in the field of forensic science, aiming to provide reference for the extraction and examination of metal evidence involved in the cases. {{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [6] |
王伟. 一种铝导线火灾熔痕的彩色金相检验方法[J]. 理化检验-物理分册, 2023, 59(7): 22-25.
(
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [7] |
陈克, 张斌, 邓松华, 等. 铜导线一次短路熔痕显微组织再结晶过程[J]. 理化检验-物理分册, 2024, 60(1): 6-11.
(
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [8] |
刘振刚, 梁国福, 张斌. 能谱分析技术在一起火灾物证溯源中的应用[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2022, 41(9): 1322-1324.
(
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [9] |
丁诗懿, 杨涵, 汪箭. 基于拉曼光谱的火烧熔痕定量鉴识技术[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2021, 40(6): 929-932.
(
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [10] |
刘义祥, 李阳, 刘彬. 铜导线短路熔痕中共晶体的定量金相研究[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2022, 41(2): 279-281.
通过模拟短路条件制备铜导线短路熔痕,对短路熔痕中共晶体进行了金相分析和定量研究。研究发现,铜导线一、二次短路熔痕共晶体组织特征具有一定区别,短路喷溅熔珠中共晶体含量分别为15.28%、5.10%,远远超过同短路类型线端熔痕中0.33%、0.19%的共晶体含量。通过对比短路熔痕中共晶体微观组织与含量大小,可以鉴别铜导线短路熔痕种类,其中喷溅熔痕的特征较明显。
(
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [11] |
李九霖, 李阳, 聂琦. 铝合金导线短路熔痕晶粒生长规律分析[J]. 热加工工艺, 2022, 51(22): 42-47.
(
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [12] |
姜文宇, 吴坚, 孙烨, 等. 过电流故障铝导线熔痕部位与组织特征关联性研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2022, 18(1): 75-80.
(
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [13] |
陈裕富. 微区痕量分析技术在火灾事故调查中的应用探究[J]. 消防界(电子版), 2017(8): 80-81.
(
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [14] |
文玉秀, 王敏. 铜导线短路熔痕的SEM/EDS分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2011, 21(6): 84-87.
(
在电气线路火灾原因的调查中,为更好地区分铜导线一次短路与二次短路的熔痕特征,用扫描电子显微镜( SEM)和X一射线能谱仪(EDS)对2种熔痕的形貌和相应的元素成分进行了试验研究.结果表明:铜导线一次短路与二次短路熔痕的表观形貌特征和元素成分具有明显的不同,二者的区别主要表现在熔痕表面所含的气孔、元素种类及导线本体与熔痕之间的过渡区方面,一次短路熔痕表面气孔多,元素种类少,导线与熔痕之间有明显界限,二次短路熔痕则相反.该研究结果可以区分短路熔痕形成的环境气氛,以此判断导线短路熔痕类型,为电气线路火灾原因的调查提供科学依据.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
 Fig.1 Grain and elemental distribution results of the copper wire base material
Fig.1 Grain and elemental distribution results of the copper wire base material Fig.2 Grain and elemental distribution results of the aluminum wire base material
Fig.2 Grain and elemental distribution results of the aluminum wire base material Fig.3 Grain distribution results of the fire-burned melt marks on copper
Fig.3 Grain distribution results of the fire-burned melt marks on copper Fig.4 Grain distribution results of short-circuit melt marks on copper wire
Fig.4 Grain distribution results of short-circuit melt marks on copper wire Fig.5 Elemental segregation distribution of fire-burned melt marks on aluminum wire
Fig.5 Elemental segregation distribution of fire-burned melt marks on aluminum wire Fig.6 Elemental segregation distribution of short-circuit melt marks on aluminum wire
Fig.6 Elemental segregation distribution of short-circuit melt marks on aluminum wire Fig.7 Typical orientation distribution (a) and polar chart (b) of fire-burned melt marks on aluminum wire
Fig.7 Typical orientation distribution (a) and polar chart (b) of fire-burned melt marks on aluminum wire Fig.8 Orientation distribution (a) and pole figure (b) of short-circuit melt marks on aluminum wire
Fig.8 Orientation distribution (a) and pole figure (b) of short-circuit melt marks on aluminum wire Fig.9 Elemental segregation distribution of fire-burned melt marks on copper wire
Fig.9 Elemental segregation distribution of fire-burned melt marks on copper wire Fig.10 Elemental segregation distribution of short-circuit melt marks on copper wire
Fig.10 Elemental segregation distribution of short-circuit melt marks on copper wire Fig.11 Orientation distribution (a) and pole figure (b) of fire-burned melt marks on copper wire
Fig.11 Orientation distribution (a) and pole figure (b) of fire-burned melt marks on copper wire Fig.12 Orientation distribution (a) and pole figure (b) of short-circuit melt marks on copper wire
Fig.12 Orientation distribution (a) and pole figure (b) of short-circuit melt marks on copper wire/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |