
May. 21, 2025

Rapid Identification of Bloodstain Based on Near Infrared Spectroscopy and Extreme Learning Machine Algorithm
BI Fulun, WANG Wei, QI Yueying, XIE Jiayi, NA Man, WU Jiaquan, LIANG Ying, ZHANG Jianqiang
Rapid Identification of Bloodstain Based on Near Infrared Spectroscopy and Extreme Learning Machine Algorithm
Bloodstain is one of the most important forensic evidences in criminal cases. How to identify the bloodstains and obtain some potential evidence is of great significance to solve the criminal case. In this paper, a hand-held near-infrared (NIR) spectrometer was used to collect the spectral data of different species of bloodstains samples on cotton fabrics with different colors including human blood, chicken blood and pig blood. After collecting the spectral data, standard normal variables (SNV) pre-processing operation was implemented on the spectral data to eliminate the common offset and scaling effects. Then, the training models were established via extreme learning machine (ELM) algorithm to identify the species of bloodstain. Next, the testing samples were predicted by means of using the built specie identification bloodstain model. Meanwhile, the traditional support vector machine (SVM) and genetic algorithm-back propagation (GA-BP) classification algorithms were also used to build the identification model and the prediction results were also compared with ELM algorithm. The experimental results showed that the prediction accuracy of ELM algorithm was 98.48%, which was higher than that of GA-BP algorithm (84.62%) and SVM algorithm (73.84%). Meanwhile, the precision, sensitivity and specificity of the prediction results using ELM algorithm were also much higher than those of SVM and GA-BP algorithms. The above results showed that the accuracy of the identification model built by ELM algorithm was the highest and the overall performance of the model was the best. The research results of the paper showed that he rapid detection method based on a handheld NIR spectrometer and ELM algorithm could identify the types of the bloodstains efficiently, non-destructively, quickly and accurately and it provided a new technical reference for bloodstains detection and identification in criminal cases.
near-infrared / extreme learning machine / bloodstain species / non-destructive / rapidly {{custom_keyword}} /
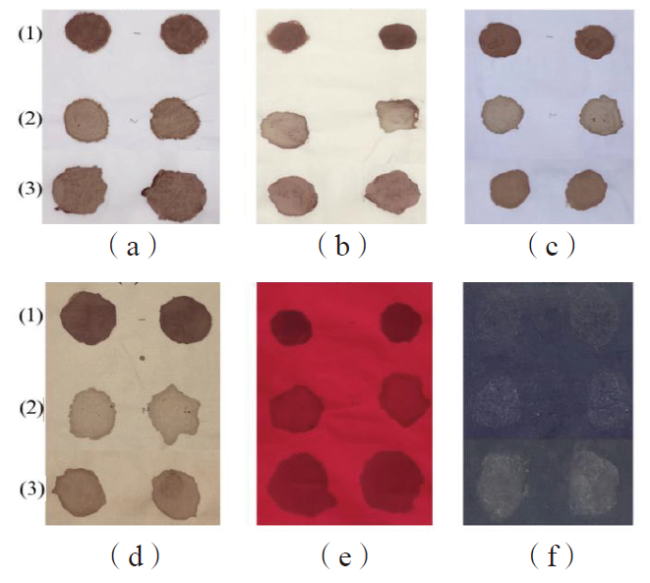
Fig.1 Blood samples on the different cotton fabric (1~3 are human blood, chicken blood and pig blood samples; a~f are the white, beige, blue, brown, red cotton and black cotton fabric)图1 不同棉织物上的血液样本(1~3分别为人血、鸡血和猪血;a~f分别是白色、米色、蓝色、棕色、红色和黑色棉织物) |
Table 1 The detail of the samples表1 样本详细信息 |
| 基底棉织物颜色 | 人血份数 | 鸡血份数 | 猪血份数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 白 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 红 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 蓝 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 米 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 棕 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 黑 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
Table 2 Accuracies with different pre-processing methods based on SVM algorithm表2 基于SVM算法的不同预处理方法精度 |
| 预处理方法 | 训练集正确率/% | 测试集正确率/% |
|---|---|---|
| SG | 60.19 | 60.18 |
| SG+D1 | 62.50 | 61.60 |
| MSC | 74.71 | 69.69 |
| SNV | 84.76 | 73.84 |
Table 3 Effects comparison of different training models for bloodstains表3 不同血迹训练模型的效果比较 |
| 客体 | 算法 | 类型 | 训练样本数 | 错误样本数 | 训练正确数 | PC/% | SN/% | SP/% | F1-score | OAC/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纺织物 | SVM | 人血 | 46 | 4 | 42 | 87.5 | 91.3 | 94.3 | 0.89 | 84.76 |
| 鸡血 | 51 | 9 | 42 | 91.3 | 82.4 | 96.0 | 0.87 | |||
| 猪血 | 54 | 10 | 44 | 77.2 | 81.5 | 86.6 | 0.79 | |||
| GA-BP | 人血 | 53 | 2 | 51 | 85.5 | 96.2 | 93.9 | 0.90 | 91.98 | |
| 鸡血 | 46 | 10 | 36 | 96.8 | 79.1 | 96.0 | 0.87 | |||
| 猪血 | 52 | 2 | 50 | 93.3 | 97.1 | 94.1 | 0.92 | |||
| ELM | 人血 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 1.00 | 100 | |
| 鸡血 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 1.00 | |||
| 猪血 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 1.00 |
| 注:PC: precision; SN: sensitivity; SP: specificity; OAC: overall accuracy。 |
Table 4 Effects comparison of different test models for bloodstains表4 不同血迹测试模型效果比较 |
| 客体 | 算法 | 类型 | 测试样本 | 测试正确数 | 错误样本数 | PC/% | SN/% | SP/% | F1-score | OAC/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纺织物 | SVM | 人血 | 26 | 17 | 9 | 85.0 | 65.4 | 92.3 | 0.74 | 73.84 |
| 鸡血 | 21 | 18 | 3 | 85.7 | 85.7 | 93.2 | 0.86 | |||
| 猪血 | 18 | 13 | 5 | 54.2 | 72.2 | 76.6 | 0.62 | |||
| GA-BP | 人血 | 19 | 17 | 2 | 81.0 | 89.5 | 91.3 | 0.85 | 84.62 | |
| 鸡血 | 26 | 18 | 8 | 90.0 | 69.2 | 94.9 | 0.78 | |||
| 猪血 | 20 | 20 | 0 | 83.3 | 100 | 91.1 | 0.91 | |||
| ELM | 人血 | 22 | 21 | 1 | 100 | 95.5 | 100 | 0.98 | 98.48 | |
| 鸡血 | 22 | 22 | 0 | 95.7 | 100 | 98.5 | 0.98 | |||
| 猪血 | 22 | 22 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 1.00 |
| [1] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [2] |
庄园, 高树辉, 谢菲, 等. 基于高光谱成像技术鉴别血痕种属的实验研究[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2022, 59(16): 474-482.
(
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [3] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [4] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [5] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [6] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [7] |
Near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy is currently the fastest-growing and the most versatile analytical method not only in the pharmaceutical sciences but also in the industry. This review focuses on recent NIR applications in the pharmaceutical technology. This article covers monitoring, by NIR, of many manufacturing processes, such as granulation, mixing or drying, in order to determine the end-point of these processes. In this paper, apart from basic theoretical information concerning the NIR spectra, there are included determinations of the quality and quantity of pharmaceutical compounds. Some examples of measurements and control of physicochemical parameters of the final medicinal products, such as hardness, porosity, thickness size, compression strength, disintegration time and potential counterfeit are included. Biotechnology and plant drug analysis using NIR is also described. Moreover, some disadvantages of this method are stressed and future perspectives are anticipated.Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [8] |
Non-destructive identification and subsequent age estimation of blood stains are significant steps in forensic casework. The latter can provide important information on the temporal aspects of a crime. As previously shown, visible spectroscopy of blood stains on white backgrounds can successfully be used for their identification and age estimation. The use of this technique however, is hampered by dark backgrounds. In the present study the feasibility to use near infrared (NIR) spectroscopy was evaluated for blood stain identification and age estimation on dark backgrounds. Using NIR reflectance spectroscopy, blood stains were distinguished from other substances with 100% sensitivity and 100% specificity. In addition, Partial Least Squares Regression analysis was applied to estimate the age of blood stains on colored backgrounds. The age of blood stains up to 1 month old was estimated successfully with a root mean squared error of prediction of 8.9%. These findings are an important step toward the practical implementation of blood stain identification and age estimation in forensic casework, where a large variety of backgrounds can be encountered.Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [9] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [10] |
陆思源, 陆志海, 王水花, 等. 极限学习机综述[J]. 测控技术, 2018, 37(10): 3-9.
(
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [11] |
翟敏, 张瑞, 王宇. 极限学习机(ELM)网络结构调整方法综述[J]. 西安文理学院学报(自然科学版), 2014, 17(1): 1-6.
(
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [12] |
崔雷涛, 陈亮, 马强. 基于在线序列极限学习机的车牌字符识别方法[J]. 微型机与应用, 2015, 34(23): 30-32.
(
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [13] |
张志洁, 侯睿. 基于极限学习机的脑卒中患病风险预测模型研究[J]. 电脑编程技巧与维护, 2022(6): 54-55, 113.
(
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [14] |
秦传波, 冯宝, 谌瑶. 基于主成分分析法和极限学习机的尿沉渣图像识别算法研究[J]. 现代电子技术, 2019, 42(11): 45-49.
(
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [15] |
高云峰, 张金萍. 基于LMD-PSO-ELM的轴承故障诊断与识别[J]. 沈阳化工大学学报, 2022, 36(5): 428-437.
(
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [16] |
王亚, 周孟然, 闫鹏程, 等. 基于极限学习机的矿井突水水源快速识别模型[J]. 煤炭学报, 2017, 42(9): 2427-2432.
(
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [17] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [18] |
沈欢超, 耿莹蕊, 倪鸿飞, 等. 近红外光谱技术结合教与学算法优化极限学习机实现烤烟等级判定[J]. 分析测试学报, 2022, 41(7): 1052-1057.
(
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [19] |
张伏, 王新月, 崔夏华, 等. 高光谱结合极限学习机的玉米品种鉴别[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2023, 43(9): 2928-2934.
(
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [20] |
邢凌宇, 王巧云, 杨磊, 等. 基于拉曼光谱和改进极限学习机的葡萄糖浓度检测[J]. 光散射学报, 2020, 32(2): 159-165.
拉曼光谱技术由于其快速、简单且无损等优势,广泛地应用于组分的定量分析。目前常用的定量回归方法包括偏最小二乘、人工神经网络、支持向量机等,为寻求新方法,本文对41组葡萄糖样本的拉曼光谱数据研究,以极限学习机为定量回归基础,结合遗传算法、粒子群算法、人工蜂群算法等优化算法,比较分析后提出一种新型自适应差分进化的人工蜂群算法应用于极限学习机,该模型对差分进化的变异率和交叉率做了调整,能够降低极限学习机容易陷入局部最优和差分进化对参数依赖性大的问题,优化后模型的评价指标较传统极限学习机和基于其它优化算法都有显著提升。实验表明,基于自适应差分进化人工蜂群算法的极限学习机提高了预测精确度和模型稳健性。
(
Raman spectroscopy is widely used in the quantitative analysis of components because of its advantages of fast, simple and nondestructive. Currently, quantitative analysis methods of Raman spectroscopy include Partial Least Squares, Artificial Neural Network, Support Vector Machine, etc. In order to seek new methods, in this paper, the Raman spectroscopy data of 41 groups glucose samples were studied. The Extreme Learning Machine was used for quantitative regression. The optimization algorithms such as Genetic Algorithm, Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm and Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm were used to improve it. After comparison and analysis,a new type of model was proposed, which called Self Adaption Differential Evolution Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm applied to the Extreme Learning Machine. The model adjusted the mutation rate and crossover rate of differential evolution,which can reduce the influence of the Extreme Learning Machine on local optimization and the differential evolution on parameter dependence. Comparing with the traditional Extreme Learning Machine and other optimization algorithm models, the optimized model evaluation index had a significant boost. Experiment showed that Extreme Learning Machine based on Self Adaption Differential Evolution Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm improved the prediction accuracy and model robustness.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [21] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [22] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [23] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [24] |
The extreme learning machine (ELM) is an efficient way to build single-hidden-layer feedforward networks (SLFNs). However, its fault tolerant ability is very weak. When node noise or node failure exist in a network trained by the ELM concept, the performance of the network is greatly degraded if a countermeasure is not taken. However, this kind of countermeasure for the ELM or incremental learning is seldom reported. This paper considers the situation that a trained SLFN suffers from the coexistence of node fault and node noise. We develop two fault tolerant incremental ELM algorithms for the regression problem, namely node fault tolerant incremental ELM (NFTI-ELM) and node fault tolerant convex incremental ELM (NFTCI-ELM). The NFTI-ELM determines the output weight of the newly inserted node only. We prove that in terms of the training set mean squared error (MSE) of faulty SLFNs, the NFTI-ELM converges. Our numerical results show that the NFTI-ELM is superior to the conventional ELM and incremental ELM algorithms under faulty situations. To further improve the performance, we propose the NFTCI-ELM algorithm. It not only determines the output weight of the newly inserted node, but also updates all previously trained output weights. In terms of training set MSE of faulty SLFNs, the NFTCI-ELM converges, and it is superior to the NFTI-ELM.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [25] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [26] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [27] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [28] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
 Fig.1 Blood samples on the different cotton fabric (1~3 are human blood, chicken blood and pig blood samples; a~f are the white, beige, blue, brown, red cotton and black cotton fabric)
Fig.1 Blood samples on the different cotton fabric (1~3 are human blood, chicken blood and pig blood samples; a~f are the white, beige, blue, brown, red cotton and black cotton fabric) Table 1 The detail of the samples
Table 1 The detail of the samples Fig.2 Structure of extreme learning machine
Fig.2 Structure of extreme learning machine Fig.3 Confusion matrix
Fig.3 Confusion matrix Fig.4 Comparison of NIR spectral between human blood on different cotton fabrics and standard human blood
Fig.4 Comparison of NIR spectral between human blood on different cotton fabrics and standard human blood Table 2 Accuracies with different pre-processing methods based on SVM algorithm
Table 2 Accuracies with different pre-processing methods based on SVM algorithm Fig.5 The original spectral data (a) and pre-processing results (b)
Fig.5 The original spectral data (a) and pre-processing results (b) Table 3 Effects comparison of different training models for bloodstains
Table 3 Effects comparison of different training models for bloodstains Table 4 Effects comparison of different test models for bloodstains
Table 4 Effects comparison of different test models for bloodstains/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |