第一作者简介:李鹏,男,山东齐河人,学士,警务技术四级主管,研究方向为理化检验鉴定。E-mail:1032888468@qq.com
将红外差谱技术应用到掺蔗糖冰毒的检验中,解决蔗糖对甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐谱峰干扰问题,实现对掺蔗糖冰毒的快速定性分析。按不同质量比例配制蔗糖和甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐样品,分别进行红外光谱检验,利用红外差谱技术处理分析样品的红外谱图,与甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐标准品进行匹配比对。结果表明在冰毒掺蔗糖比例≤90%时,红外差谱技术能够很好扣除蔗糖谱峰对甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐谱峰的干扰,得到与甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐标准品匹配度高的红外光谱图;掺蔗糖比例大于90%时,差谱后的谱库可以得到甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐的部分特征峰。利用红外差谱技术可以很好地对掺蔗糖冰毒检材进行快速定性分析,并对检材中掺蔗糖的比例做出预估。
Infrared spectroscopy is widely used in drug inspection owing to its simple and rapid operation, low detection cost, green environmental protection and other advantages. There are relevant technical specifications about infrared spectroscopy for drug inspection and identification, especially on occurrence of mass sampling cases where an important role would be played with it to greatly improve the efficiency of detection and reduce the cost of handling cases. However, the adulterated drugs, often encountered in actual cases, will cause interference to the spectrum peaks of tested drugs with those of adulterated substances, hence bringing difficulties to both the qualitative analysis of drugs and rapidity. Even, if the adulterated substances accounted for large proportion, the spectrum peaks of adulterated substances would suppress the drug’s, putting the role of infrared spectroscopy being restricted or incapable. Fortunately, infrared differential spectroscopy is functional of distinguishing different components in mixture so that it can be applied to qualitatively analyze the material components in mixture. Here, the infrared differential spectroscopy was tried to test the sucrose-adulterated methamphetamine hydrochloride. Sampling sucrose and methamphetamine hydrochloride were prepared under different mass ratios, successively having been tested by infrared spectroscopy to get their infrared spectra. The obtained infrared spectra were processed and analyzed into infrared differential spectroscopy, with comparison against those from the standard sample of methamphetamine hydrochloride. When the ratio of sucrose to methamphetamine hydrochloride was ≤90%, the infrared differential spectroscopy could well eliminate the peaks of sucrose interfering to those of methamphetamine hydrochloride, capable of harvesting infrared spectrums with high matching degree to standard methamphetamine hydrochloride. When the proportion of sucrose was greater than 90%, some characteristic peaks of methamphetamine hydrochloride can be still obtained through the differential spectrum library. The infrared differential spectroscopy can be used for rapid qualitative analysis of methamphetamine adulterated with sucrose, able to predict the proportion of sucrose in the tested material although it can not make accurate qualitative analysis when sucrose accounted for proportion too high. For thorough comprehensive analysis, it is necessary to combine detections of GC/MS, LC/MS and other analytical choices, and carefully draw conclusions to prevent misjudgment.
红外光谱法由于操作简单快速、检测成本低、绿色环保等优点, 被广泛应用于毒品检验[1], 利用红外光谱法检验毒品已有相关检验鉴定技术规范, 尤其在大样本案件的检验中, 发挥着重要作用, 极大地提高了检案效率, 节约了办案成本[2, 3, 4, 5, 6]。但在实际案件检验中, 经常会遇到掺假的毒品, 由于掺假物质的谱峰会对毒品谱峰造成干扰, 给毒品快速定性带来困难, 尤其是掺假比例较大时, 掺假物质谱峰对毒品峰干扰严重, 影响对检材的快速定性分析, 红外光谱法受到了一定制约。红外差谱技术具有辨别混合物中不同成分的功能, 可应用于混合物中物质成分的定性分析。市售冰毒通常为甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐, 甲基苯丙胺又称去氧麻黄素。蔗糖由一分子葡萄糖的半缩醛羟基与一分子果糖的半缩醛羟基彼此缩合脱水而成, 分为白砂糖、赤砂糖、绵白糖、冰糖、粗糖等。本研究利用红外光谱仪采集掺加不同比例蔗糖的混合冰毒的数据后, 采用红外差谱技术对谱图进行处理, 通过调整差谱系数, 排除所掺加蔗糖的干扰, 得到与甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐标准品匹配较好的谱图。利用红外差谱技术, 可以为红外光谱法检验掺蔗糖冰毒提供帮助。
傅里叶红外光谱仪(Thermo Scientific Nicolet iN10)、玛瑙研钵(Thermo Fisher Scientific); 甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐(北京芬格尔安科技有限公司)、蔗糖(本实验选用舒可曼白砂糖)。
测试附件:iZ10衰减全反射(ATR)附件; 扫描范围:4 000~650 cm-1; 扫描次数:16次; 分辨率:4 cm-1。
分别取蔗糖和甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐样品, 用研钵研磨成粉末。取研磨粉末配制质量比如表1所示的实验样品, 用研钵混合均匀, 供红外光谱仪分析。
| 表1 样品配制比例 Table 1 Samples and preparation ratios |
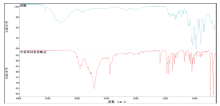
利用红外光谱可以快速准确对蔗糖和甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐粉末样品进行定性分析。对蔗糖和甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐样品进行红外光谱分析, 结果见图1。蔗糖的主要特征峰有3 306 、2 942、1 427、1 343、1 237、987、908、732、680 cm-1。甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐的主要特征峰有2 734、2 513、2 461、2 060、1 455、1 387、1 191、1 046、700 cm-1等, 2 734、2 513、2 461、2 060 cm-1同时存在为甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐的标志谱带[7]。
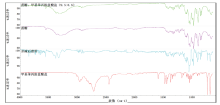
掺加蔗糖比例在40%及以下时, 甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐的多数特征峰都有很好的峰形峰位, 并且可以通过谱库检索快速识别。经差谱技术处理后, 甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐的峰形更好, 谱库检索时匹配度更高。以掺加40%蔗糖为例作对比如图2, 直接检索匹配度为70以上, 处理后匹配度在90左右。检索谱库建库方法与本研究样品采集模式不同, 匹配度相对较低。用相同方法建立检索库或者用红外自带的质量检查功能分析, 匹配度可达99。
掺加蔗糖比例在40%~90%之间时, 随着蔗糖掺入量的增加, 受蔗糖特征峰的影响, 甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐的特征峰受干扰更严重, 无法通过谱库检索快速识别。在经差谱技术处理后, 扣除蔗糖特征峰的干扰, 可得到很好的甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐的光谱图, 可以通过特征峰识别, 也可以通过谱库检索快速识别。以掺加90%蔗糖为例作对比如图3, 直接检索结果为蔗糖匹配度最高, 处理后匹配度最高为甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐, 匹配度为60~70。用相同方法建立检索库或者用红外自带的质量检查功能分析, 匹配度高于70。
当掺加蔗糖比例为90%以上时, 通过差谱技术得到的光谱图无法通过谱库检索得到较高匹配度的结果, 但是可以得到甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐的部分特征峰, 以掺加95%蔗糖为例(图4)。依据此类红外谱图结果, 可为GC-MS或LC-MS定性和定量检验提供参考。
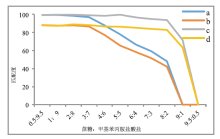
在红外谱图分析软件谱库管理中, 新建掺蔗糖冰毒检索谱库。把表1中13个不同比例样品的红外光谱图加入掺蔗糖冰毒谱库。不同混合比例样品的红外光谱图进行差谱处理, 对差谱处理前后的谱图, 分别进行自建库和系统自带库检索。对检索结果中与甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐的匹配度制作折线图(图5), a为差谱前自建库匹配检索, b为差谱前系统自带库匹配检索, c为差谱后自建库匹配检索, d为差谱后系统自带库匹配检索。由图可见, 差谱后检索匹配结果明显优于差谱处理前; 自建库匹配度高于系统自带谱图库。当冰毒掺加蔗糖比例小于等于90%时, 差谱后可以很好地对甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐成分定性。当冰毒掺加蔗糖比例达到90%时, 在库里无法匹配到甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐, 差谱后还能有较好红外谱图, 可以与甲基苯丙胺盐酸盐有较好的匹配结果。谱图差谱处理前, 掺加物质高于50%时无法通过谱库检索命中目标物; 经差谱处理后, 掺加物质低于90%时可以通过谱库检索命中目标物。
本文以冰毒掺加蔗糖为例讲解红外差谱的应用, 但红外差谱技术的应用不局限于冰毒掺加蔗糖。在实际案例中, 会经常遇到掺加各类物质的毒品, 有的甚至直接以掺假剂替代毒品进行贩卖, 在红外光谱检验时, 利用差谱技术可以很好地解决此类检验问题。但是掺假物质比例小于10%时要结合GC-MS法、LC-MS法等分析手段综合分析, 慎重下结论, 防止出现错判误判。
数据库的建立可为快速鉴定毒品种类及掺假物质提供支持。建库时要考虑建立不同毒品及掺假物质、不同掺假比例、多种掺假物质模型的数据库。利用数据库, 一方面可以快速定性毒品和掺假物质, 另一方面可以预估毒品掺假的比例, 为下一步定量分析及溯源推断提供帮助。
红外光谱仪自带自动差谱功能, 但掺假比例不同差谱的效果会有不同。如果自动差谱的谱图效果不好, 可以通过调节差减系数得到理想的谱图, 差减系数可调范围为-500~500, 粗调可调刻度为5, 细调可调刻度为0.000 1。如果差谱后出现倒峰, 先选择粗调差减系数, 调整整体峰形, 突出目标物特征峰; 再选择细调差减系数, 调整谱峰细节。
不同的红外光谱仪, 其检测器、检测模式、参数设定会有差异, 得到的红外光谱图峰位会有所差异。在红外光谱峰谱库比对和参考文献时, 应注意此类问题的影响。
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|