第一作者简介:刘永涛,男,河北石家庄人,硕士,副高级警务技术任职资格,研究方向为毒物毒品检验。E-mail: liuyongtao518@163.com
目的 建立超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法同时测定血液和尿液中15种降糖药物(二甲双胍、维达列汀、苯乙双胍、罗格列酮、西他列汀、吡格列酮、甲苯磺丁脲、妥拉磺脲、格列吡嗪、格列齐特、格列本脲、格列美脲、那格列奈、格列喹酮、瑞格列奈)的分析方法。方法 分别用乙腈对血液和尿液样品沉淀蛋白过膜后,采用超高效液相色谱-三重四级杆质谱联用仪测定。色谱柱为Agilent Eclipse Plus C18色谱柱(2.1 mm×100 mm×3.5 µm),有机相为0.1%甲酸甲醇溶液,水相为5 mmol/L乙酸铵和甲酸水溶液,进行梯度洗脱;流速为0.3 mL/min,采用电喷雾正离子模式,选择反应监测方式(SRM)检测。结果 15种药物在血液和尿液中在低浓度(0.5~10 ng/mL)至高浓度(200~1000 ng/mL)范围内线性关系良好, R2均大于0.998。二甲双胍提取回收率为28.1%~42.9%,其余14种降糖药物提取回收率在60.8%~119.0%之间;二甲双胍在尿液中检出限为5 ng/mL,其余14种药物在血液和尿液中的检出限均低于2 ng/mL。15种药物在血液和尿液三种添加浓度中日内和日间精密度相对标准偏差RSD均不高于8.9%( n=6)。结论 该方法检测灵敏度高、速度快、专属性高、重复性好,可用于生物样品血液和尿液中15种降血糖药物的同时检测。
Objective To establish an ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS) method for determination of 15 hypoglycemic drugs (metformin, vildagliptin, phenformin, rosiglitazone, sitagliptin, pioglitazone, tolbutamide, tolazamide, glipizide, gliclazide, glyburide, glimepiride, nateglinide, gliquidone, repaglinide) in blood and/or urine.Methods The blank control samples of both blood and urine were spiked with the selected drugs, then purified with acetonitrile to precipitate the proteins, successively having subjected to the analysis of UPLC-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) under the conditions: LC operation was performed through an Agilent Eclipse Plus C18 column (2.1mm×100mm×3.5µm) that was eluted with the mobile phases consisting of water containing 0.1% formic acid plus 5mmol/L ammonium acetate (A) and methanol containing 0.1% formic acid (B) at the flow rate of 0.3mL/min; MS operation was run at the selected reaction monitoring (SRM) in electrospray positive ion mode.Results An adequate linearity was afforded at concentrations from the lower limit of quantification (0.5-10ng/mL) to the upper limit of quantification (200-1000 ng/mL), with the coefficients of determination ( R2) being higher than 0.998. The extraction recoveries of 14 hypoglycemic drugs ranged from 60.8% to 119.0%, with exception of the metformin’s showing from 28.1% to 42.9%. The detection limits of 14 drugs were lower than 2ng/mL in blood and urine, leaving the metformin’s being 5ng/mL in urine. The 15 drugs unveiled their relative standard deviations (RSD) relating to intra-/inter-day precisions were less than 8.9% with the addition of three concentrations into the blood and urine (n=6).Conclusions The method is of high sensitivity, high speed, high specificity and good reproducibility, capable of detecting the selected 15 hypoglycemic drugs in biological samples of blood and urine.
口服降糖药主要包括磺酰脲类、格列奈类、双胍类、噻唑烷二酮类、α -糖苷酶抑制剂等治疗药物。降血糖药在控制血糖的同时常引发一些药品不良反应[1], 有些甚至可以导致死亡。目前, 不法分子利用降血糖药物实施犯罪导致受害人低血糖休克甚至死亡的刑事案件, 以及利用降血糖药物自杀的案件时有发生, 尤其是磺酰脲类降血糖药物, 因此, 降糖药的检测需列入到毒物检测的常见范围。当前, 亟需建立一种灵敏度较高、能同时检验多种常用降血糖药物的检测方法, 补充法医毒物对非正常死亡案件中死者生物检材中降血糖药物常规检测空白, 从而为相关非正常死亡案件死因判断提供一定的判断依据。降血糖类化合物的检测方法包括免疫法[2]、拉曼光谱法[3, 4]、薄层色谱法[5, 6, 7, 8]、液相色谱质谱联用法[9, 10, 11]等, 由于液相色谱质谱联用法具有准确性强、灵敏度高等特点, 是司法鉴定实验室选用的最佳检测技术。目前液相色谱质谱法检测多种类降糖药针对的检材多为中药材和保健品[12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18], 对于血液中的降糖药多为单类降糖药的检测[10, 11], 国内同时对多类降糖药进行液相色谱质谱检测的报道较少, 尿液的相关报道更为少见。
本研究采用乙腈沉淀蛋白法、高效液相色谱-串联质谱技术(UPLC-MS), 建立了二甲双胍、维达列汀、苯乙双胍、罗格列酮、西他列汀、吡格列酮、甲苯磺丁脲、妥拉磺脲、格列吡嗪、格列齐特、格列本脲、格列美脲、那格列奈、格列喹酮、瑞格列奈等4类15种常用降血糖药物在血液和尿液中的快速检测方法, 方法简便快捷、灵敏准确、重复性好, 完全满足日常检测, 能为临床中毒检测及司法鉴定提供参考。
UltiMate 3000型超高效液相色谱(美国 Thermo Fisher Scientific公司); TSQ Endura三重四级杆串联质谱仪(美国 Thermo Fisher Scientific公司)。
甲醇、乙腈、甲酸和乙酸铵(色谱纯, 中国Dikma公司); 二甲双胍、维达列汀、苯乙双胍、罗格列酮、西他列汀、吡格列酮、甲苯磺丁脲、妥拉磺脲、格列吡嗪、格列齐特、格列本脲、格列美脲、那格列奈、格列喹酮、瑞格列奈等标准品(纯度≥ 99%; 中国Dikma公司); 去离子水(“ 屈臣氏” 纯净水)。
分别准确称取二甲双胍、维达列汀、苯乙双胍、罗格列酮、西他列汀、吡格列酮、甲苯磺丁脲、妥拉磺脲、格列吡嗪、格列齐特、格列本脲、格列美脲、那格列奈、格列喹酮、瑞格列奈标准品适量, 用甲醇溶解并配制成1.0、0.01、0.001 mg/mL三种浓度的单标和混标溶液。
移取血液、尿液等液体样品1.0 mL, 于15 mL具盖离心管中, 加入乙腈3.0 mL, 混匀后, 超声10 min后, 不低于10 000 r/min离心5 min, 取上清液, 用有机微孔滤膜过滤, 进行液相色谱-串联质谱(LC-MS/MS)分析。
1.4.1 色谱条件
色谱柱:Agilent Eclipse Plus C18柱(2.1 mm× 100 mm, 3.5 µ m); 柱温:25℃; 流动相A:5 mmol/L乙酸铵和甲酸缓冲水溶液(称取乙酸铵0.384 g, 加入800 μ L甲酸, 加水溶解稀释至1 000 mL, pH值约为3), 流动相B:0.1%的甲酸甲醇; 流速:0.3 mL/min; 进样体积:10 μ L; 洗脱方式:梯度洗脱, 梯度洗脱条件见表1。
| 表1 液相色谱梯度洗脱条件 Table 1 Gradient elution conditions for liquid chromatography |
1.4.2 质谱条件
离子源:电喷雾离子源(ESI); 扫描方式:正离子模式扫描; 检测方式:选择反应监测(SRM); 喷雾电压:3 500 V; 加热(蒸发)温度:350 ℃; 鞘气及压力:氮气, 38 psi; 碰撞气及压力:氩气, 1.5 mTorr; 辅助气及压力:氮气, 10 arb; 离子传输管温度:350 ℃(见表2)。
| 表2 15种化合物的保留时间、母离子、子离子、射频电压(RF)和碰撞能量(CE) Table 2 Retention time, precursor ions, product ions, RF voltages and collision energies about the 15 compounds |
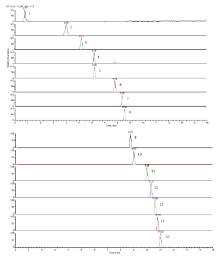
本实验利用15种化合物的空白添加样品分别对乙腈-水和甲醇-水作为流动相进行考察, 结果甲醇-水响应值高于乙腈-水。对有机相分别不添加甲酸和添加0.1%甲酸, 水相添加0.1%甲酸(pH≈ 2.5)、0.1%乙酸铵(pH≈ 3.5)、5 mmol/L的乙酸铵和甲酸缓冲液(pH≈ 3), 结果以0.1%甲酸甲醇和5 mmol/L的乙酸铵和甲酸缓冲液作为流动相, 使得妥拉磺脲、维达列汀的响应值明显得到提升, 并且可以使本实验进行的15种降糖药物达到良好的分离效果, 响应值较高。在优化的色谱条件下, 15种化合物的SRM色谱图见图1, 色谱峰相对应化合物见表2。
本实验对血液和尿液检材采用乙腈沉淀蛋白和Oasis® PRIME HLB固相萃取柱的两种前处理方法进行了比较, 发现二者提取回收率和检出限基本相当, 所以选择乙腈沉淀蛋白法。同时也对检材超声时间进行了比较, 实验结果发现对样品进行10 min超声时, 回收率最高。乙腈沉淀蛋白法操作简单、快捷, 并且节约成本, 完全满足实际办案需要。
利用15种浓度为0.001 mg/mL的化合物单标溶液, 对每一种化合物分别进行分析, 分别在正、负离子模式下进行扫描, 利用仪器自带软件进行自动筛选优化母离子及子离子, 选取相对丰度较高的两个离子分别作为定量和定性离子, 并在SRM模式下对响应最弱的一种化合物进行喷雾电压、离子源温度等参数进行优化。结果表明, 15种化合物在正离子模式下响应强度和峰形都优于负离子模式。
2.4.1 线性关系
分别对空白血液和尿液进行0.5、1、2、5、10、20、50、100、200、500、1 000 ng/mL的添加, 进行样品前处理后, 以化合物的峰面积(y)为纵坐标、对应的添加浓度为横坐标(x, ng/mL)绘制标准曲线。结果表明, 15种药物在血液和尿液中在低浓度(0.5~10 ng/mL)至高浓度(200~1 000 ng/mL)范围内线性关系良好, R2均大于0.998, 见表3。
| 表3 15种化合物的线性方程、R2和检出限 Table 3 Linear equations, correlation coefficients and detection limits of the 15 compounds |
2.4.2 方法检出限
分别对空白血液和尿液进行0.5、1、2、5、10 ng/mL的样品添加后, 对15种化合物记录峰面积并计算信噪比, 信噪比(S/N)数值在50左右时, 作为该15种化合物在血液和尿液的定性检出限(表3), 除二甲双胍在尿液中检出限为5 ng/mL, 其他14种药物的检出限均低于2 ng/mL, 考虑二甲双胍应该与基质影响有关, 如案件需要, 可以适当增加检材量或对萃取液进行浓缩后检测。
2.4.3 提取回收率
分别对空白血液和尿液进行5、50、100和10、50、100 ng/mL的添加, 按1.3前处理方法进行样品前处理, 除二甲双胍提取回收率为28.1%~42.9%, 其他14种降糖药物提取回收率为60.8%~119.0%之间(表4)。这与Lam等[19]研究报道二甲双胍在尿液中提取回收率较低相印证, 其利用Oasis® HLB 固相萃取柱萃取, 提取回收率为24%。由于二甲双胍服用剂量较大, 副作用较小, 通常每次用量范围为250~1000 mg, 用此检测方法对临床服用该药物人员血液及尿液进行了检验, 效果良好, 完全可以满足实际案例检测要求。
| 表4 15种化合物在血液和尿液中的提取回收率和精密度 Table 4 Recoveries and precisions of the 15 compounds in blood and urine |
2.4.4 方法精密度
分别对空白血液和尿液进行5、50、100 ng和10、50、100 ng的添加, 按1.3前处理方法进行样品前处理, 每个样品分别连续进样6次, 连续进样3 d, 分别记录峰面积, 结果表明各化合物峰面积日内和日间的相对标准差(RSD)均不高于8.9%(见表4)。
本研究针对司法鉴定中常规生物检材血液和尿液, 建立了高效液相色谱-质谱联用法同时测定15种降血糖药物的分析方法。本方法操作简便、准确、灵敏, 扩展了常规临床中毒检测及司法鉴定药物检测范围, 为利用降糖药自杀或犯罪的治安案件及刑事案件提供技术支持。
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|