第一作者简介:杨发震,男,云南大理人,学士,工程师,研究方向为毒物毒品及微量物证。E-mail:382561515@qq.com
目的 建立了缴获毒品及非法添加的中草药样品中曲马多、芬太尼和地芬诺酯同时定量分析的高效液相色谱-二极管阵列(HPLC-DAD)检测方法。方法 样品经甲醇溶解超声提取后,采用Agilent Zorbax SB-C18 (4.6mm×250mm, 5μm) 色谱柱分离,12mmol/L磷酸二氢钾(10%稀磷酸调至pH=4)/乙腈梯度洗脱,在210nm波长下检测。结果 结果显示该3种待测成分检出限(S/N=3)在0.2 ~0.5μg/mL间、定量限(S/N=10)在0.5 ~1.0μg/mL间;在2~700μg/mL范围内线性关系良好, R2均大于0.999;黄色、白色粉末状毒品中三个浓度(所测样品原始含量的80%、100%、120%)平均加标回收率在99.6%~105.4%间,相对标准偏差(RSD%, n=6)小于1.4%;日间精密度在1.19%~2.11%间,重复性测试在0.31%~1.43%间,稳定性测试在0.29%~0.87%间。结论 该方法操作简单、准确,精密度、稳定性好,能够用于缴获毒品及非法添加的中草药样品中曲马多、芬太尼和地芬诺酯含量的定量分析。
Objective To establish an HPLC-DAD method for simultaneously quantitative analysis of tramadol, fentanyl and diphenoxylate in seized drugs and/or illegally-added herbal medicines.Methods The sample was dissolved into methanol and extracted under ultrasonic, having the obtained analytes separated through an Agilent Zorbax SB-C18 (4.6×250mm, 5μm) column that was flowed with gradient-eluting of 12mM potassium dihydrogen phosphate buffer (pH=4 adjusted by 10% dilute phosphoric acid)/acetonitrile. The analysis was completed in 30 minutes and detected at the wavelength of 210nm.Results The three chemical substances were shown of their detection limits (S/N=3) and quantitation limits (S/N=10) among 0.2~0.5μg/mL and 0.5~1.0 μg/mL, respectively. The linear relationship was good in the range of 2~700μg/mL, with the correlation coefficients ( R2) being all greater than 0.999, the three-concentration average recoveries (80%, 100%, 120%) in yellow and white powdery drugs among 99.6%~105.4%, the relative standard deviations (RSD%, n=6) being less than 1.4%, the inter-day precisions among 1.19%~2.11%, the repeatability within 0.31%~1.41%, and the stability being fallen into 0.29%~0.87%.Conclusions The method is simple, accurate, precise and stable, capable of quantitative analysis of tramadol, fentanyl and diphenoxylate in seized drugs and/or illegally-added herbal medicines.
近年来, 在实际案件的检验鉴定中, 经常碰到嫌疑人将曲马多、芬太尼和地芬诺酯等非法添加到中草药或地芬诺酯单独添加制成不同颜色的复方胶囊作为阿片类毒品戒断药物或新型毒品销售的案件, 并且已发生多起吸食过量导致死亡的案件。
曲马多(tramadol)是一种阿片受体激动剂和常用的中枢性镇痛药, 最早于1977年在德国上市, 它易产生不良反应且存在滥用的可能性[1, 2], 其体内代谢产物主要是O-去甲基曲马多(ODT)、N-去甲基曲马多(NDT)及N, O-去甲基曲马多(NODT)成分[3, 4], 由于获取途径方便、价格便宜, 近年已被一些不法分子作为传统毒品替代品来使用[5]。芬太尼(fentanyl)血浆中的治疗水平可低至1 ng/mL, 药效约为吗啡的50~100倍、海洛因的30~50倍, 是一种强效、短效的麻醉性镇痛药, 主要用于外科麻醉和癌症患者疼痛的治疗, 最早于20世纪70年代中期出现滥用, 主要代谢物为诺芬太尼[6, 7, 8]。芬太尼被添加到海洛因中的历史可追溯到1979年, 目前白色海洛因、黑焦油海洛因等中均有芬太尼及类似物检出的报告, 仅在2013~2014年间, 美国就有700多人死于芬太尼及类似物[9, 10, 11]。地芬诺酯(diphenoxylate)长期服用可形成依赖, 常被吸毒人员作为海洛因替代品滥用, 中毒量与治疗量较接近且代谢产物地芬诺辛毒性更强, 过量服用极易引起中毒甚至死亡, 目前滥用的情况越来越严重[12, 13, 14, 15, 16]。有报道称伊朗销售的许多用作阿片类药物戒断药的中草药中, 大量样品检出曲马多、美沙酮和地芬诺酯成分[17]。
目前血液、血浆、尿液、毛发等生物样品中曲马多、芬太尼、地芬诺酯成分的检验, 主要采用气相色谱-质谱法(GC-MS)、液相色谱-串联质谱法(LC-MS)、高效液相色谱法(HPLC)、液相色谱-高分辨质谱法(LC-HRMS)、气相色谱-高分辨质谱法(GC-HRMS)及毛细管电泳法(CE)等[4, 5, 7, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26]。体外样品如片剂、针剂溶液等所含曲马多、芬太尼、地芬诺酯的检验主要采用高效液相色谱法(HPLC)、毛细管电泳法(CE)进行[27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34]。目前尚未见有对缴获的毒品样品尤其是中草药毒品样品中曲马多、芬太尼、地芬诺酯三种成分同时定量测定的方法报道。
本文建立了对缴获毒品中曲马多、芬太尼、地芬诺酯同时定量分析的高效液相色谱-二极管阵列(HPLC-DAD)检验方法, 可为相关案件的检验鉴定提供方法上的支撑。该方法前处理简便、准确, 精密度、稳定性好, 已成功应用于实际案件缴获的不同颜色胶囊包装的黄色粉末状中草药毒品和白色粉末状毒品样品的定量分析。图1为曲马多、芬太尼、地芬诺酯三种物质的结构式。
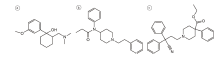 | 图1 曲马多(a)、芬太尼(b)和地芬诺酯(c)的化学结构式Fig.1 The chemical structures of tramadol (a), fentanyl (b) and diphenoxylate (c) |
Agilent 1260 Infinity II液相色谱系统, 配二极管阵列检测器(美国Agilent 公司), Purelab Flex纯水系统(英国ELGA公司), MS 105分析天平(瑞士Mettler Toledo公司), KQ-50DB型超声波清洗器(昆山市超声仪器有限公司)。
盐酸曲马多(化学对照品, 约100 mg, 中国药品生物制品检定所), 盐酸地芬诺酯(化学对照品, 约50 mg, 中国药品生物制品检定所), 枸橼酸芬太尼(国家药品标准物质, 约100 mg, 中国食品药品检定研究院), 甲醇和乙腈(HPLC级, 美国Fisher Scientific公司), 磷酸(分析纯, 西陇科学股份有限公司), 磷酸二氢钾(分析纯, 天津风船化学试剂科技有限公司), 实验用水为超纯水。
准确配制浓度为1.0 mg/mL的曲马多、芬太尼、地芬诺酯单标标准储备液及混标标准储备液, -20 ℃恒温避光保存, 实验时, 用甲醇稀释成所需浓度的单标或混标标准工作液。
案件中抽取的不同颜色胶囊包装的毒品65份, 按照胶囊颜色(胶囊帽-胶囊体)分为7种颜色:蓝-白色、金-金色、棕-棕色、黑-黄色、红-白色、黑-白色、蓝-蓝色, 其中包括41份黄色粉末状中草药毒品(编为S-1至S-41号)和24份白色粉末状毒品(编为S-42至S-65号)。
41份黄色粉末状中草药毒品胶囊中:有16份为蓝-白色、8份为金-金色、11份为棕-棕色、6份为黑-黄色包装; 24份白色粉末状毒品胶囊中:有5份为棕-棕色、5份为红-白色、7份为黑-白色、7份为蓝-蓝色包装。选取编为S-1号黄色粉末状中草药毒品和S-43号白色粉末状毒品用于相关测试。
上述均为某市公安局禁毒部门在2019年1月至2020年3月份期间在四川、重庆、陕西、云南等地缴获并委托本实验室检验的样品, 样品抽取后于室温保存。
本实验室采用气相色谱-质谱联用技术对上述样品定性检验后发现, 黄色粉末状中草药毒品中均含有曲马多、芬太尼和地芬诺酯成分, 白色粉末状毒品中均含有地芬诺酯成分。
分别准确称取黄色粉末状毒品50 mg、白色粉末状毒品10 mg, 加适量甲醇超声提取20 min后, 加甲醇定容至10 mL, 摇匀, 过0.22 μ m微孔滤膜, 供HPLC-DAD分析。
色谱柱:Agilent Zorbax SB-C18 色谱柱 (4.6 mm× 250 mm, 5 μ m); 柱温:30 ℃。流动相A:12 mmol/L磷酸二氢钾(10%稀磷酸调至pH=4), 流动相B:乙腈。梯度洗脱程序:0.0~3.0 min, 23.5%B; 3.0~8.0 min, 37%B; 8.0~12.0 min, 37%B; 12.0~18.0 min, 80%B; 18.0~23.0 min, 80%B; 23.0~25.0 min, 23.5%B。流速:0.8 mL/min; 进样量为5 μ L。检测波长:210 nm, 采集范围:190~400 nm。
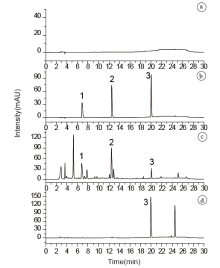
实验考察了以0.3%磷酸溶液/乙腈、0.3%甲酸溶液/乙腈和12 mmol/L磷酸二氢钾溶液(10%稀磷酸调至pH=4)/乙腈等流动相在等度及梯度洗脱条件对待测目标物(曲马多、芬太尼及地芬诺酯)保留时间、峰型和分离度等的影响, 结果采用12 mmol/L磷酸二氢钾溶液(10%稀磷酸调至pH=4)/乙腈为流动相、梯度洗脱时该3种目标物能够成功分离。通过对该流动相流速、梯度等条件优化, 结果在1.4所述条件下进行测试的实际样品中(10份黄色粉末状中草药毒品和10份白色粉末状毒品样品)目标物与相邻的杂质成分色谱峰达到基线分离, 分离度均大于1.5。在190~400 nm波长范围内进行扫描时, 相同浓度曲马多在210 nm处的吸收(峰面积)为220 nm的一半, 地芬诺酯和芬太尼最大吸收均为210 nm, 为了方便起见, 最终选择检测波长为210 nm。图2为曲马多、芬太尼和地芬诺酯的吸收波长, 图3为黄色粉末状中草药毒品、白色粉末状毒品样品和混标标准甲醇液(0.1 mg/mL)的典型色谱图。
 | 图2 曲马多(左)、芬太尼(中)和地芬诺酯(右)的紫外吸收波长Fig.2 UV absorption wavelengths of tramadol (left), fentanyl (middle) and diphenoxylate (right) |
配制系列浓度的混标标准工作液对该3种目标化合物进行检出限(S/N=3)、定量限(S/N=10)测试, 线性范围使用2~700 μ g/mL浓度范围进行测试, 每个浓度进行6次平行实验。结果如表1所示, 曲马多的检出限与定量限分别为0.5、1.0 μ g/mL, 芬太尼、地芬诺酯的检出限均为0.2 μ g/mL, 定量限均为0.5 μ g/mL; 在2~700 μ g/mL范围内呈现良好的线性, R2均大于0.999。
| 表1 曲马多、芬太尼、地芬诺酯的线性方程、决定系数、线性范围、检出限和定量限(n=6) Table 1 Linear equations, determination coefficients, linearity ranges, limits of detection (LODs) and limits of quantification (LOQs) for determination of tramadol, fentanyl, diphenoxylate by HPLC-DAD (n=6) |
回收率测试采用标准加入法, 并用其结果评价方法的准确性。用建立的方法测定出典型黄色粉末状中草药毒品(S-1)和白色粉末状毒品(S-43)原始含量, 将三种不同浓度(约为S-1和S-43中各成分原始含量的80%、100%和120%)单标标准溶液准确添加到S-1和S-43样品中, 按照1.3样品前处理后进行测定, 每个浓度平行6次实验。按照以下公式计算回收率:回收率=(测得量-原始量)/加入量× 100%, 结果如表2所示, S-1号中草药毒品中曲马多、芬太尼和地芬诺酯的平均回收率在99.6%~105.4%间, S-43号白色粉末状毒品中地芬诺酯的平均回收率为100.2%, 所有化合物的相对标准偏差均小于1.40%, 表明该方法准确性好。
| 表2 黄色粉末状中草药毒品(S-1)和白色粉末状毒品(S-43)中曲马多、芬太尼及地芬诺酯的回收率(n=6) Table 2 Recoveries of tramadol, fentanyl and diphenoxylate derived from HPLC-DAD (Yellow powdered herbal medicine: sample 1; white powdered drug: sample 43) (n=6) |
连续3日测定不同浓度混标标准工作液(浓度为10、100、700 μ g/mL)的含量, 每日平行测定6次, 用相对标准偏差评估其方法的日内和日间精密度, 结果如表3所示, 该3种目标化合物日内精密度(RSD%, n=6)在0.64%~1.59%间, 日间精密度(RSD%, n=18)在1.19%~2.11%间, 表明所建方法精密度良好。
| 表3 三种不同浓度条件下曲马多、芬太尼和地芬诺酯的日内和日间精密度 Table 3 Intra- and inter-day precision of three different-concentration tramadol, fentanyl and diphenoxylate derived from HPLC-DAD |
分别测定平行制备的黄色粉末状中草药毒品(S-1)和白色粉末状毒品(S-43)溶液, 用校准曲线计算其含量, 用相对标准偏差(RSD)表示方法的重复性。结果如表4所示, S-1和S-43中目标化合物的相对标准偏差(RSD%, n=6)在0.31%~1.43%间, 方法重复性良好。
| 表4 黄色粉末状中草药毒品(S-1)和白色粉末状毒品(S-43)中曲马多、芬太尼和地芬诺酯的重复性测试(n=6) Table 4 Repeatability of tramadol, fentanyl and diphenoxylate analyzed with HPLC-DAD (Yellow powdered herbal medicine: sample 1; white powdered drug: sample 43) (n=6) |
分别于0、2、4、6、8、12、24 h测定制备的黄色粉末状中草药毒品(S-1)和白色粉末状毒品(S-43)溶液, 记录其峰面积, 用相对标准偏差(RSD)表示其稳定性。结果如表5所示, S-1和S-43中目标化合物的相对标准偏差(RSD%, n=7)在0.29%~0.87%间, 表明制备的样品溶液在24 h内稳定。
| 表5 黄色粉末状中草药毒品(S-1)和白色粉末状毒品(S-43)中曲马多、芬太尼和地芬诺酯的24 h峰面积稳定性 Table 5 Peak area stability of tramadol, fentanyl and diphenoxylate determined within 24 hours with HPLC-DAD (Yellow powdered herbal medicine: sample 1; white powdered drug: sample 43) |
应用该方法对不同颜色胶囊包装的65份实际案件样品进行了定量分析, 每份样品平行测定2次。结果如表6所示, 所有黄色粉末状中草药毒品中, 蓝-白色、棕-棕色胶囊中:地芬诺酯的含量远低于曲马多和芬太尼的含量, 蓝-白色胶囊中曲马多和芬太尼两者含量大致相似, 棕-棕色胶囊中曲马多含量均是芬太尼含量的2倍以上; 金-金色、黑-黄色胶囊中:地芬诺酯远高于曲马多和芬太尼的含量, 且大部分样品芬太尼是曲马多含量的2倍以上。所有白色粉末毒品中, 红-白色胶囊中地芬诺酯含量均低于0.19 mg/mg, 棕-棕色胶囊中地芬诺酯含量均高于0.36 mg/mg, 黑-白、蓝-蓝色胶囊中地芬诺酯含量在0.24~0.30 mg/mg间。
| 表6 实际案件检材中曲马多、芬太尼及地芬诺酯的定量结果 Table 6 Quantitation of tramadol, fentanyl and diphenoxylate analyzed from an actual forensic case |
本文建立了同时定量分析缴获毒品及非法添加的中草药样品中曲马多、芬太尼和地芬诺酯含量的HPLC-DAD方法, 该方法简单、准确, 精密度、稳定性良好, 回收率高。并将该方法成功应用于实际案件中缴获的毒品样品及非法添加的中草药样品中曲马多、芬太尼和地芬诺酯含量的检验, 因毒品样品种类繁多, 杂质成分差异大, 该方法能否适用于其他基质的样品有待日后进一步研究。
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|