第一作者简介:林葭,女,福建福州人,博士,高级工程师,研究方向为刑事技术理化检验。E-mail:12645923@qq.com
目的 建立人血中丁醚脲及其代谢产物丁醚脲-脲和丁醚脲-甲烷亚胺的高效液相色谱-飞行时间质谱联用(HPLC-QTOF/MS)分析方法。方法 取人血2mL,用2mL 乙腈沉淀蛋白,选用Kinelex® Cl8(2.6μm 3.0mm×100mm)色谱柱,以0.1%甲酸+乙腈(A相)和5mmol/L 甲酸铵溶液+0.1%甲酸溶液(B相)为流动相梯度洗脱分离,采用液相色谱-飞行时间质谱仪的电喷雾电离,正离子模式进行分析。结果 该方法人血中的丁醚脲、丁醚脲-脲和丁醚脲-甲烷亚胺检出限分别为1.0、0.1、1.0 ng/mL;丁醚脲、丁醚脲-脲、丁醚脲-甲烷亚胺在0.5~100ng/mL范围内线性良好 ( R2=0.9991~0.9996),在3个浓度水平平均回收率为78.1%~98.5%,日内精密度为4.1%~5.5%,日间精密度为5.5%~9.0% 。结论 该方法样品前处理方法操作简便,专属性强、灵敏度较高,适用于人血中丁醚脲及其代谢产物的定性定量。
Objective To establish a method for analysis of diafenthiuron and its metabolic residues in blood with liquid chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (LC-QTOF/MS).Methods The blood sample (2.0mL) was extracted with acetonitrile (2.0mL) to precipitate protein, having its well-treated supernatant subjected to chromatographic separation on a Kinetex® 2.6μm C18 analytical column (100mm ×2.1mm) through which the gradient elution was run with the mobile phases consisting of 0.1% formic acid plus acetonitrile (mobile phase A) and water containing 20mM ammonium formate plus 0.1% formic acid (mobile phase B). The MS analysis was conducted with HPLC-QTOF/MS under the conditions of electrospraying positive ionization mode (ESI+).Results Diafenthiuron and its metabolites, diafenthiuron-methanimidamide and diafenthiuron-urea, delivered their respective limit of detection in each spiked blood as 1.0ng/mL, 0.1ng/mL and 1.0ng/mL, demonstrating their calibration curves being linear within the range of 0.5~100ng/mL ( R2=0.9991~0.9996), average recoveries spiked at three-level concentrations spanning among 78.1%~98.5%, and the inter- and intra-day precision falling into 4.1%~5.5% and 5.5%~9.0%, respectively.Conclusion The here-established method is simple, rapid, sensitive and specific, appropriate for identification and quantification of diafenthiuron and its metabolite residues in blood.
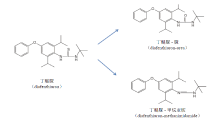
丁醚脲(diafenthiuron)是一种新型硫脲杀虫杀螨剂, 具有触杀、胃毒、内吸等作用, 广泛应用于水果、蔬菜、棉花和茶树上防治蚜虫、叶蝉、粉虱以及螨虫等[1, 2, 3], 它通过影响昆虫呼吸作用、干扰能量转换和转化为具有更高毒性的代谢产物达到杀虫目的。丁醚脲在光解、水解、环境微生物降解以及植物体内降解的主要产物为丁醚脲-甲烷亚胺、丁醚脲-脲等[4](见图1)。最新研究表明, 丁醚脲对蜜蜂具有一定毒性[5], 丁醚脲代谢物比丁醚脲原药本身具有更高的毒性, 因此2002年欧盟颁布的第2076/2002号法规规定对丁醚脲实行本地区内禁用、禁售[6]。2020年, 国内发生多起使用丁醚脲投毒和自杀的案件, 目前, 有关人血液中丁醚脲及其代谢物测定方法未见报道。本文建立了血液中丁醚脲及其代谢物的高效液相色谱质谱联用方法(HPLC-QTOF/MS), 并应用于实际案件的检测中。该方法灵敏度高, 专属性强, 适用于法庭科学中丁醚脲及其代谢物的检验鉴定。
Agilent 1290 超高效液相色谱仪-6520四级杆串联飞行时间质谱仪(美国Agilent公司), 丁醚脲、丁醚脲-甲烷亚胺、丁醚脲-脲( 美国sigma-Aldrich 公司); 乙酸乙酯、甲醇、乙腈(色谱纯, 德国Merck 公司), 甲酸、甲酸铵(分析纯, 美国Tedia 公司)、水(法国Millipore 超纯水系统制得)。血液样本取自本实验室近期未服药的健康人员。
选用Kinelex® Cl8(3.0 mm×100 mm, 2.6 μm)色谱柱; 柱温:30 ℃; 流动相A:0.1%甲酸+乙腈, 流动相B:5 mmol/L 甲酸铵溶液+0.1%甲酸溶液; 进样量2 μL; 流速为0.3 mL/min梯度洗脱, 梯度洗脱程序见表1。
| 表1 梯度洗脱条件 Table 1 Gradient elution conditions |
离子源:ESI; 扫描方式:正离子全扫描; 全扫描范围:m/z 50~1 700, 毛细管电压:4 000 V; 毛细管电压:130 V, 锥孔电压:60 V; 氮气, 气体温度:350 ℃, 干燥气流速:8 L/min, 喷雾器压力:35 psi; 碎裂电压:175 V。
丁醚脲中毒案件中死者血液2 mL, 置于15 mL具塞管中, 加入2 mL乙腈, 振荡3 min, 超声3 min, 8 000 r/min离心5 min, 取上层清液过0.22 μm有机微孔滤膜于试管中, 60 ℃氮吹至近干, 用1 mL乙腈溶液定容, 取0.1 mL定容溶液于有内衬管的棕色进样瓶中。
在空白血中分别加入不同量的丁醚脲、丁醚脲-甲烷亚胺、丁醚脲-脲标准溶液, 配制成0.5、1、2、5、10、20、50、100 ng/mL的丁醚脲、丁醚脲-甲烷亚胺、丁醚脲-脲血液样品, 并按照1.4法处理后进样。以待测物浓度为横坐标, 待测物的峰面积为纵坐标, 进行回归运算, 求得直线回归方程, 即为标准曲线。
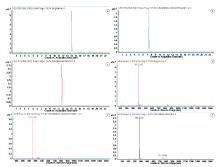
分别测定20 ng/mL丁醚脲、丁醚脲-甲烷亚胺、丁醚脲-脲的空白血液添加标准品溶液, 各组分的保留时间、精确分子质量、理论分子质量和质量误差见表2, 各组分的提取离子流色谱图及质谱图见图2。
| 表2 丁醚脲及其代谢产物的检测参数 Table 2 Mass spectrum parameters of diafenthiuron and its metabolite residues |
将无丁醚脲及其代谢物接触史的健康人血液2 mL作为基质, 按照1.4法处理后进样。在目标物的位置无响应, 说明空白基质无干扰, 方法选择性良好。
本研究血液中的丁醚脲、丁醚脲-脲、丁醚脲-甲烷亚胺在0.5~100.0 ng/mL范围内线性良好, 线性回归方程分别为y=2×106x+40 958(R2=0.999 1)、y=107x +148 437(R2=0.999 6)、y=107x -28 874(R2=0.999 1)。本方法确定的丁醚脲、丁醚脲-脲、丁醚脲-甲烷亚胺的LOD分别为1.0、0.1、1.0 ng/mL, LOQ均为5.0 ng/mL, 可以满足法医毒物分析工作的需要。
分别在空白血液中添加1、10、100 ng/mL丁醚脲、丁醚脲-脲、丁醚脲-甲烷亚胺标准品, 配制成低、中、高3个浓度水平的质控样品。每天取各浓度水平的样品6个进行测定, 连续4 d, 计算日内和日间测定的准确度及精密度。准确度为测定平均值与参照值的百分比, 计算丁醚脲、丁醚脲-脲、丁醚脲-甲烷亚胺峰面积的相对标准偏差(RSD)作为日内精密度, 再重复3 d, 计算RSD值作为日间精密度(见表3)。方法的日间及日内精密度均小于10%, 准确度为89.0%~101.1%。
| 表3 方法的准确度、精密度、基质效应和提取回收率 Table 3 Accuracies, precisions, matrix effects and recoveries |
丁醚脲、丁醚脲-脲、丁醚脲-甲烷亚胺分别制备1、10、100 ng/mL 3个浓度的控制样品, 每个浓度6份, 按照1.4法处理后进样, 测得目标物的峰面积为A1。空白血液经1.4法处理后, 加入丁醚脲、丁醚脲-脲、丁醚脲-甲烷亚胺, 制成相应浓度的溶液, 测得其峰面积为A2。提取回收率=A1/A2×100%。另取相同量的对照品溶液, 测得丁醚脲、丁醚脲-脲、丁醚脲-甲烷亚胺的峰面积为A3。基质效应=A2/A3×100%。由表3可见丁醚脲、丁醚脲-脲、丁醚脲-甲烷亚胺的提取回收率均在75%以上, 说明丁醚脲、丁醚脲-脲、丁醚脲-甲烷亚胺在样品前处理过程中损失较少。
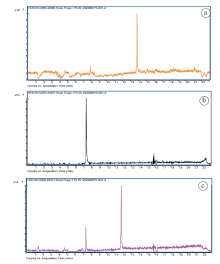
2020年6月福建省漳州市发生了一起造成两死两伤的投毒案件, 运用所建立的方法, 从其中一名死者在医院仅存的3 mL血液中检出了丁醚脲、丁醚脲-脲、丁醚脲-甲烷亚胺, 该死者血液中出现与丁醚脲、丁醚脲-脲、丁醚脲-甲烷亚胺标准保留时间相同(保留时间偏差在±0.1%之内), 定性分析精确质量数相同的色谱峰, 且空白尿液无干扰, 浓度分别为0.12、1、0.02 μg/mL(图4)。该检验结果与嫌疑人的供述一致。
本文采用乙腈提取-高效液相色谱串联飞行时间质谱方法, 建立了一种血液中丁醚脲、丁醚脲-脲、丁醚脲-甲烷亚胺的分析方法。实验结果表明该方法具有较高的排除基质干扰能力以及灵敏度优势, 完全能满足司法鉴定实践中对血液中丁醚脲、丁醚脲-脲、丁醚脲-甲烷亚胺的分析。
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|