第一作者简介:华锋,男,河南驻马店人,硕士研究生,研究方向为痕迹检验技术。E-mail: 1096350592@qq.com
目的 探究鞋内底足迹的显出情况及可能影响显现效果的因素,寻找有效的鞋内底足迹显现方法。方法 收集PU材质的皮鞋鞋垫、EVA材质的运动鞋鞋垫、解放牌胶鞋鞋垫共144只,用多波段光源法、茚二酮法、茚三酮法三种方法分别对穿用时间为一周、一个月、三个月、六个月的鞋内底足迹进行显现,按照显现方法、材质、穿用时间进行分类讨论并对数据进行统计和分析。结果 采用多波段光源法、茚二酮法、茚三酮法分别成功显出15、14、19例,有效显出率分别为31.25%、29.17%、39.58%,PU材质、EVA材质、解放牌胶鞋三种材质分别成功显出15、23、10例,有效显出率分别为31.25%、47.92%、20.83%,穿用时间为一周、一个月、三个月、六个月的检材分别成功显出3、6、13、26例,有效显出率分别为8.33%、16.67%、36.11%、72.22%。多波段光源法、茚二酮法、茚三酮法对鞋内底足迹显出率的影响,其差异无明显统计学意义;EVA材质运动鞋鞋内底足迹显出率高于PU材质皮鞋鞋内底足迹显出率,高于解放牌胶鞋鞋内底足迹显出率,并且差异具有统计学意义;穿用时间长的检材显出率高于穿用时间短的检材并且差异具有统计学意义。结论 鞋内底足迹的显现效果与鞋内底材质、穿用时间因素有关,多波段光源法、茚二酮法、茚三酮法均能对鞋内底足迹有效显出。
Objective To analyze the effect of developing insole footprint and the potentially influential factors so as to find an effective method to develop insole footprint.Methods 144 insoles (products of three kinds of stuff: the PU-material one trampled with leather shoes, the EVA-material one trodden with sports shoes, and the one worn with Jiefang rubber shoes) were collected after they were respectively put under feet for a week, one month, three and/or six months. All the insoles were individually examined with multiband light source, indandione and ninhydrin to reveal whether footprint was appeared in the insole examined. The footprints were rated of their developing effect according to the chosen method, the material, wearing time and development, resulting in their classified results being discussed and the obtained data being undertaken of statistics.Results There were respective 15, 14 and 19 footprints developed on insoles with the corresponding disposal of multiband light source, indandione and ninhydrin, showing their each effective developing rate of 31.25%, 29.17% and 39.58%. The insoles made from PU, EVA and ones for Jiefang rubber shoes successfully had the respective 15, 23 and 10 footprints developed, leaving the effective developing rates of 31.25%, 47.92% and 20.83%. Time-different wearing durations of one week, one month, three and/or six months caused the respective 3, 6, 13 and 26 footprints developed successfully, demonstrating their effective developing rates of 8.33%, 16.67%, 36.11% and 72.22%. There was no significant difference to develop footprint on insole among the disposals of multiband light source, indandione and ninhydrin. EVA-material insoles were of highest footprint developing rate, with the PU kind and the insoles for Jiefang rubber shoes being at the second and third places, having brought forth a statistical significance among them. Longer wearing time was of statistical significance in footprint developing rate against the short time.Conclusion The developing effect of footprint on insole is related to the material of insole and wearing time. Three developing approaches of multiband light source, indandione and ninhydrin are all able to develop insole footprint effectively.
在现场勘查中, 鞋子是常见的痕迹物证。经过一定穿用时间后, 可能会在鞋内底上留下反映穿鞋人脚型特征的印痕, 该印痕与赤足足底具有一定的对应性, 在足迹检验中具有较高的利用价值。然而在自然光状态下, 人肉眼难以清晰地观察到反映在鞋内底上的足迹形态, 通常需要借助一定的方法将其显现出来。
我国目前对鞋内底足迹的研究较少, 现有的理论主要包括鞋内底足迹的形成机制、检验方法等[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7], 对鞋内底足迹显现方法的研究只涉及物理光学的方法。汪旭峰等[1]发现使用254 nm短波紫外光源进行照明可以使鞋内底上汗液成分遗留较多的部位形成强烈反射, 由于鞋内底材质的不同, 显现拍摄的效果略有差异。
国外目前对鞋内底足迹的研究主要集中于将鞋内底足迹和穿鞋人油墨捺印赤足迹的差异性进行比较[8, 9], Hammer等[8]发现了同一人和不同人鞋内底足迹和油墨捺印赤足迹在形态特征上表现出的同一性和差异性。本文尝试采用多波段光源法、茚二酮法、茚三酮法对不同材质、不同穿用时间鞋内底上的足迹进行显现, 分析显现方法、材质、穿用时间对显现效果的影响。
PU材质的皮鞋鞋垫、EVA材质的运动鞋鞋垫、解放牌胶鞋鞋垫(以下分别简称为“ PU” “ EVA” “ JF” ), DCSLED-Ⅱ 台式多波段光源、滤光镜、Nikon相机, 茚三酮喷显剂(北京华兴瑞安科技有限公司)、茚二酮试剂(采用常用配方)[10]。
本实验选取中国人民公安大学刑事科学技术专业的学生作为志愿者, 其每天的生活轨迹和活动范围大体相同, 整个实验过程持续了春夏秋冬四个季节。共收集得到144只鞋内底样本, 样本的构成情况如下:按照穿用时间来分类, 穿用1周、1个月、3个月、6个月的各有36只; 按照材质来分类, 三种材质的样本各有48只, 如表1所示。
| 表1 实验样本的构成情况及相应数量 Table 1 The experimental samples and testing setup |
样本分为12组, 每组样本的材质和穿用时间均相同, 样本数量都为12。然后将每一个组的12个样本平均分成3个亚组(每个亚组4只), 3个亚组分别用多波段光源法、茚二酮法、茚三酮法进行显现。
采用多波段光源法进行显现时, 将多波段光源调整到蓝绿激发光波段, 对样本分别进行照射, 然后将照射后的显现效果进行拍照记录。
采用茚三酮法进行显现时, 用茚三酮喷显剂对样本进行均匀适量喷涂, 在自然状态下完全晾干后, 对样本的显现效果进行拍照记录。
采用茚二酮法对样本进行显现时, 用配制好的茚二酮溶液将样本分别浸泡10~15 s, 取出完全晾干, 然后放入恒温箱中控制100 ℃、相对湿度60 %条件下烘烤10 min, 最后在暗室条件下用535 nm波长光照射, 透过红色滤光镜进行观察、拍照, 显现出的鞋内底足迹发出高强度荧光。
本文采用分级的方法, 对显现质量进行评判。主要依据显现后的足迹是否完整、边缘轮廓清晰度、形态特征明显程度将显现效果划分为四个等级, 如表2及图1所示, 其中“ +++” 和“ ++++” 等级具备鉴定价值。本文定义“ +++” 和“ ++++” 等级的样本数量之和占样本总量的百分比为有效显出率。
| 表2 鞋内底足迹显现效果分级及评判标准 Table 2 Evaluation criteria on grading the effect of developing insole footprint |
2.1.1 多波段光源法
采用多波段光源法共显现鞋内底检材48份, 显现效果等级为“ ++++” 有7份, 显现效果等级为“ +++” 有8份, 具备鉴定价值的共有15份, 有效显出率为31.25%, 显现效果如图2、图3所示。
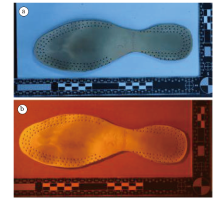 | 图2 多波段光源照射显现PU材质皮鞋鞋内底上足迹的效果(a. 照射前; b. 照射后)Fig.2 The effect of multi-band light source irradiation on developing footprint from PU-material insole (a. before irradiation; b. after irradiation) |
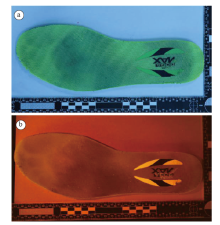 | 图3 多波段光源照射显现EVA材质运动鞋鞋内底上足迹的效果(a. 照射前; b. 照射后)Fig.3 The effect of multi-band light source irradiation on developing footprint from EVA-material insole (a. before irradiation; b. after irradiation) |
2.1.2 茚二酮法
采用茚二酮法共显现鞋内底检材48份, 显现效果等级为“ ++++” 有4份, 显现效果等级为“ +++” 有10份, 有效显出率为29.17%, 显现效果如图4所示。
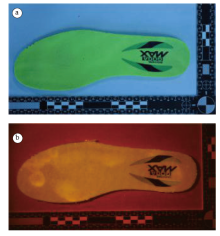 | 图4 茚二酮浸泡显现EVA材质运动鞋鞋内底上足迹的效果(a. 显现前; b. 显现后)Fig.4 The effect of indandione soaking on developing footprint from EVA-material insole (a. before visualization; b. after visualization) |
2.1.3 茚三酮法
采用茚三酮法共显现鞋内底检材48份, 显现效果等级为“ ++++” 有5份, 显现效果等级为“ +++” 有14份, 有效显出率为39.58%, 显现效果如图5所示。
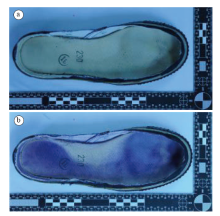 | 图5 茚三酮喷显胶鞋鞋内底上足迹的效果(a. 显现前; b. 显现后)Fig.5 The effect of ninhydrin spraying on developing footprint from Jiefang rubber shoes’ insole (a. before visualization; b. after visualization) |
多波段光源法、茚二酮法、茚三酮法三种方法对于鞋内底足迹均能取得良好的显现效果。采用χ 2检验分析显现方法与可鉴定率, 无统计学差异(χ 2=1.313, P > 0.05)。
2.2.1 PU材质
PU材质皮鞋鞋内底检材共48份, 显现效果等级为“ ++++” 有5份, 显现效果等级为“ +++” 有10份, 有效显出率为31.25%。
2.2.2 EVA材质
EVA材质皮鞋鞋内底检材共48份, 显现效果等级为“ ++++” 有6份, 显现效果等级为“ +++” 有17份, 有效显出率为47.92%。
2.2.3 JF材质
解放牌胶鞋鞋内底检材共48份, 显现效果等级为“ ++++” 有5份, 显现效果等级为“ +++” 有5份, 有效显出率为20.83%。
三种不同材质的鞋内底足迹能通过一定的方法被不同程度地显出, 且显现效果具有明显差异, EVA材质运动鞋鞋内底足迹的有效显出率最高, 解放牌胶鞋鞋内底足迹的有效显出率最低。采用χ 2检验分析鞋内底材质与可鉴定率, 其差异具有统计学意义(χ 2=8.063, P < 0.05)。
穿用时间为一周的检材共36份, 显现效果等级为“ ++++” 有0份, 显现效果等级为“ +++” 有3份, 有效显出率为8.33%。
穿用时间为一个月的检材共36份, 显现效果等级为“ ++++” 有2份, 显现效果等级为“ +++” 有4份, 有效显出率为16.67%。
穿用时间为三个月的检材共36份, 显现效果等级为“ ++++” 有6份, 显现效果等级为“ +++” 有7份, 有效显出率为36.11%。
穿用时间为六个月的检材共36份, 显现效果等级为“ ++++” 有8份, 显现效果等级为“ +++” 有18份, 有效显出率为72.22%。
随着穿用时间的增长, 显现效果也不断提升。穿用时间越长的鞋内底足迹显现效果越好, 有效显出率越高。穿用时间为一周时, 只有极少数的鞋内底足迹显现效果能达到鉴定条件, 穿用时间为六个月时, 绝大部分的鞋内底足迹显现效果都能达到鉴定条件。采用χ 2检验分析穿用时间与可鉴定率, 其差异具有统计学意义(χ 2 =39.250, P < 0.01)。
多波段光源法、茚二酮法、茚三酮法三种方法对于鞋内底足迹均能取得良好的显现效果, 且有效显出率无明显差异。
鞋内底足迹的显现效果与鞋内底材质、穿用时间因素有关。三种不同材质的鞋内底足迹能通过一定的方法被不同程度显出, 且显现效果具有明显差异, 显出的EVA材质运动鞋鞋内底足迹的有效显出率最高, 解放牌胶鞋鞋内底足迹的有效显出率最低。随着穿用时间的增长, 显现效果也不断提升。穿用时间为一周时, 只有极少数的鞋内底足迹显现效果能达到鉴定条件, 穿用时间为六个月时, 绝大部分的鞋内底足迹显现效果都能达到鉴定条件。当技术人员在实际工作中遇到穿用时间较短的鞋内底时, 仍应该细心进行处理和利用, 可能会为案件侦破提供意想不到的证据支撑。
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|