作者简介: 陈明,工程师,学士,研究方向为理化检验。 E-mail: 782790929@qq.com
目的 建立自制烟火药爆炸残留物中氯酸钾、雄黄和雌黄等主要成分的激光拉曼光谱检验法。方法 用激光拉曼光谱仪在烟火药爆炸残留物的微区中寻找炸药颗粒并进行原位检验,同时用炸药组分标准物质做对照检验,然后将烟火药爆炸残留物中的炸药颗粒拉曼光谱图与标准物质拉曼光谱图进行对照来定性。结果 用该方法检验自制烟火药中的氯酸钾、雄黄、雌黄拉曼光谱图与标准物质拉曼光谱图一致,雄黄和雌黄能明显区分。结论 本文所建立的方法简便、快速、准确,适用于自制烟火药爆炸残留物中炸药成分的检验。
Objective To establish a method for detecting potassium chlorate, realgar and orpiment in homemade fireworks explosive residues by laser Raman spectrum.Methods The explosive particles in the micro-area on the picked-up homemade fireworks explosive residues were searched and tested in situ by laser Raman spectrometer, with the standard substances of explosive components as the reference for comparison at the same time. The qualitative decision was made based on the consistency of their Raman spectrograms.Results The Raman spectra of potassium chlorate, realgar and orpiment were obtained from the picked-up samples of a case, showing that potassium chlorate is of better peak shape by its strong displacement at 938.35 nm (base peak), 977.54 nm and 487.07 nm; whereas the Raman shift of realgar is mainly located between 400-100 nm, specifically, the 233.24 nm (base peak), 344.38 nm (where a shoulder is appeared in its wide-peak shape), 186.04 nm and 271.92 nm; but for orpiment, its Raman shift is mainly at 341.59 nm (base peak, the largest peak shape compared with the latter two), 228.88 nm and 183.42 nm. Through the literature to prove that peaks at 233 nm and 186nm ascribe to the As-As-As stretching and that at 344 nm to the S-As-S stretching, together with the consistency of Raman spectrograms of standard potassium chlorate, realgar and orpiment to the corresponding one of the respective substance in the homemade fireworks explosive residues, the main components of the homemade fireworks explosive in the involved case are not only defined but realgar and orpiment can also be clearly distinguished by the Raman analyzer test.Conclusions Raman microscopy technology can be directly used for the qualitativeness about the components of explosives through their comparison with the relevant standard substances. Besides, this method can also determine the specific configuration of realgar. Taken together, the method is suitable for detection of the homemade fireworks explosives and their residues.
激光拉曼光谱法结合了激光、显微技术和拉曼技术的优点。激光具有单色性好、方向性强和功率密度高等优点, 采用激光作为发射光源大大提高了拉曼光谱的激发效应; 同时利用显微技术, 能够将激光准确聚焦到微区样品上, 排除其他物质的干扰[1]。拉曼位移仅与被测物分子能级有关, 不同价态、不同分子结构、不同晶体结构物质的拉曼位移不相同, 拉曼光谱范围为4 000~40 cm-1, 可参照标准物质对无机物进行检测分析。因此可以充分利用激光拉曼显微技术对爆炸残留物中微量炸药成分进行定性检验[2, 3], 目前在黑火药的检验中已有成功应用[4, 5]。四川省自制烟火药中多用氯酸钾和硫磺, 也有用雄黄或雌黄代替硫磺, 常规化学检验和离子色谱法检验无法直接对氯酸钾、雄黄和雌黄进行定性。本文利用激光拉曼显微技术对自制烟火药爆炸残留物中的氯酸钾、雄黄和雌黄进行了分析定性, 能够将雄黄和雌黄区分开来。
2014年6月6日, 一住户家中发生爆炸, 致其家中3岁小孩的右手及脸部被炸伤。现场提取疑似爆炸金属片、瓷砖上粘附的黑色不明物、人体脱落组织、伤者脸颊内嵌入的竹签及黑色颗粒等物证材料。采用激光拉曼显微技术对检材进行了检验, 具体如下。
仪器设备:Thermo DXR激光显微拉曼光谱仪(美国Thermo Fisher公司), 配10倍目镜, 10倍、20倍、50倍、100倍长焦物镜, 532 nm激光波长发生器, 近红外增强型CCD检测器。
实验条件:532 nm激光, 激光能量调至5 mW, 光阑25μ m狭缝, 数据采集范围3500~100 cm-1, 曝光时间5 s、次数8。
标准样品:雄黄(As4S4, 英国PCL公司, 99.0 %), 雌黄(As2S3, 英国PCL公司, 99.0 %), 氯酸钾(KClO3, 天津科密欧化学试剂有限公司, AR)。
检测方法:用532 nm激光分别对检材样品和标准品进行拉曼光谱分析。
经激光拉曼仪检测, 在检材金属片上残留物颗粒中获得了峰形较好的几组特征峰的拉曼光谱谱图。
部分残留物颗粒在1 000~400 nm范围内可见一组类似氯酸钾的拉曼位移特征峰, 分别在938.35 (基峰)、977.54和487.07 nm有较强位移, 峰形较好, 见图1。
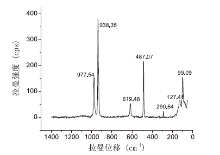 | 图 1 金属片上残留物中类似氯酸钾的拉曼光谱图Fig.1 Raman spectrogram of potassium-chlorate-like substance in the residue on the picked-up metal slice |
部分残留物颗粒在400~100 nm范围内有一组类似雄黄的拉曼位移特征峰, 分别在233.24(基峰)、344.38、186.04、271.92 nm有较强位移, 其中344.38 nm有肩峰, 且峰形较宽, 见图2。
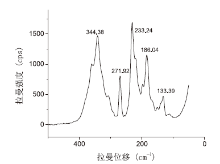 | 图 2 金属片上残留物中类似雄黄的拉曼光谱图Fig.2 Raman spectrogram of realgar-like substance in the residue on the picked-up metal slice |
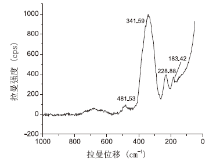 | 图 3 金属片上残留物中类似雌黄的拉曼光谱图Fig.3 Raman spectrogram of orpiment-like substance in the residue on the picked-up metal slice |
部分残留物颗粒在600~150nm范围内有一组类似雌黄的拉曼位移特征峰, 分别在341.59(基峰)、228.88和183.42 nm有较强位移, 其基峰峰形宽大, 其他峰相对较小, 见图3。
用激光拉曼仪对氯酸钾、雄黄、雌黄标准物质进行检验, 其拉曼光谱图与检材金属片上残留物颗粒中烟火药成分拉曼光谱图均能较好匹配。
在1000~400 nm范围内检材中部分残留物颗粒与氯酸钾标准物质均有相同的特征峰形, 且特征峰拉曼位移及拉曼强度比相似, 谱图对比见图4。
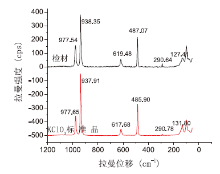 | 图 4 金属片上残留物颗粒与氯酸钾标准物质对比拉曼光谱图Fig.4 Comparison of Raman spectrogram of standard potassium chlorate with that obtained from the picked-up sample |
在400~100 nm范围内检材中部分残留物颗粒与雄黄标准物质均有相同的特征峰形, 其中在344 nm处检材和标准物质峰均有肩峰, 经查阅资料[6], 233和186 nm为As-As-As伸缩振动, 344 nm为S-As-S伸缩振动, 且特征峰拉曼位移及拉曼强度比相似, 谱图对比见图5。
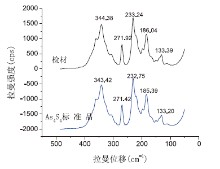 | 图 5 金属片上残留物颗粒与雄黄标准物质对比拉曼光谱图Fig.5 Comparison of Raman spectrogram of standard realgar with that obtained from the picked-up sample |
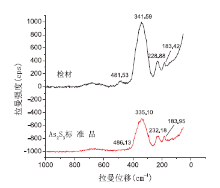 | 图 6 金属片上残留物颗粒与雌黄标准物质对比拉曼光谱图Fig.6 Comparison of Raman spectrogram of standard orpiment with that obtained from the picked-up sample |
在450~150 nm范围内检材中部分残留物颗粒与雌黄标准物质均有相同的特征峰形, 在341~335 nm处的基峰峰形均较宽大, 且特征峰拉曼位移及拉曼强度比相似, 谱图对比见图6。
检材中部分残留物颗粒的拉曼位移分别与氯酸钾、雄黄、雌黄标准物质拉曼位移相似, 且匹配较好, 拉曼位移对比见表1。
| 表 1 检材和标准品中的氯酸钾、雄黄、雌黄拉曼位移 Table 1 Raman shifts of potassium chlorate, realgar and orpiment in either the picked-up sample or the standard substance |
结合谱图特征峰峰形、拉曼位移和拉曼强度比, 在该案检材金属片的残留物颗粒中分别检出了烟火药成分氯酸钾、雄黄和雌黄。
本案例由于雄黄和雌黄没有标准谱图, 故利用标准物对雄黄和雌黄进行对比定性。不过, 雌黄标准品与检材的拉曼位移有偏差, 这主要因雌黄4个特征峰峰型不好, 最大峰取值位置不同所致。雄黄和雌黄属于共生体, 在雄黄标准品检验中发现有极少量的雌黄存在, 同样在雌黄标准品检验中也发现有极少量的雄黄存在。这概因雄黄可通过As2S2虚拟结构转化为雌黄之故[7]。雄黄有4种构型, 分别为α -As4S4, β -As4S4, χ -As4S4以及para-realgar的副雄黄或者拟雄黄。本案中的雄黄经与资料[8]对比, 可认定其构型归属于副雄黄。
近年来, 四川某地发生数起自制烟火药爆炸事故, 从爆炸残留物中检出的大多为氯酸钾和雄黄, 但本案例除检出氯酸钾和雄黄外, 还检出了较大量的雌黄, 说明所用原料不同, 有一定的特殊性。
利用激光拉曼显微技术对物质成分进行直接定性, 克服了化学法检验无法直接得到物质成分及其结构的缺点, 对实际检案很有价值。
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|


